API
epoll提供给用户进程的接口有如下四个,本文基于linux-5.1.4源码详细分析每个API具体做了啥工作,通过UML时序图理清内核内部的函数调用关系。
int epoll_create1(int size);
创建一个epfd句柄,size为0时等价于int epoll_create(0)。
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event);
向epfd上添加/修改/删除fd。
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int maxevents, int timeout);
返回所有就绪的fd。
内核数据结构
先上一张UML类图,从整体进行把握,图中已经标出各个数据结构所在的文件。
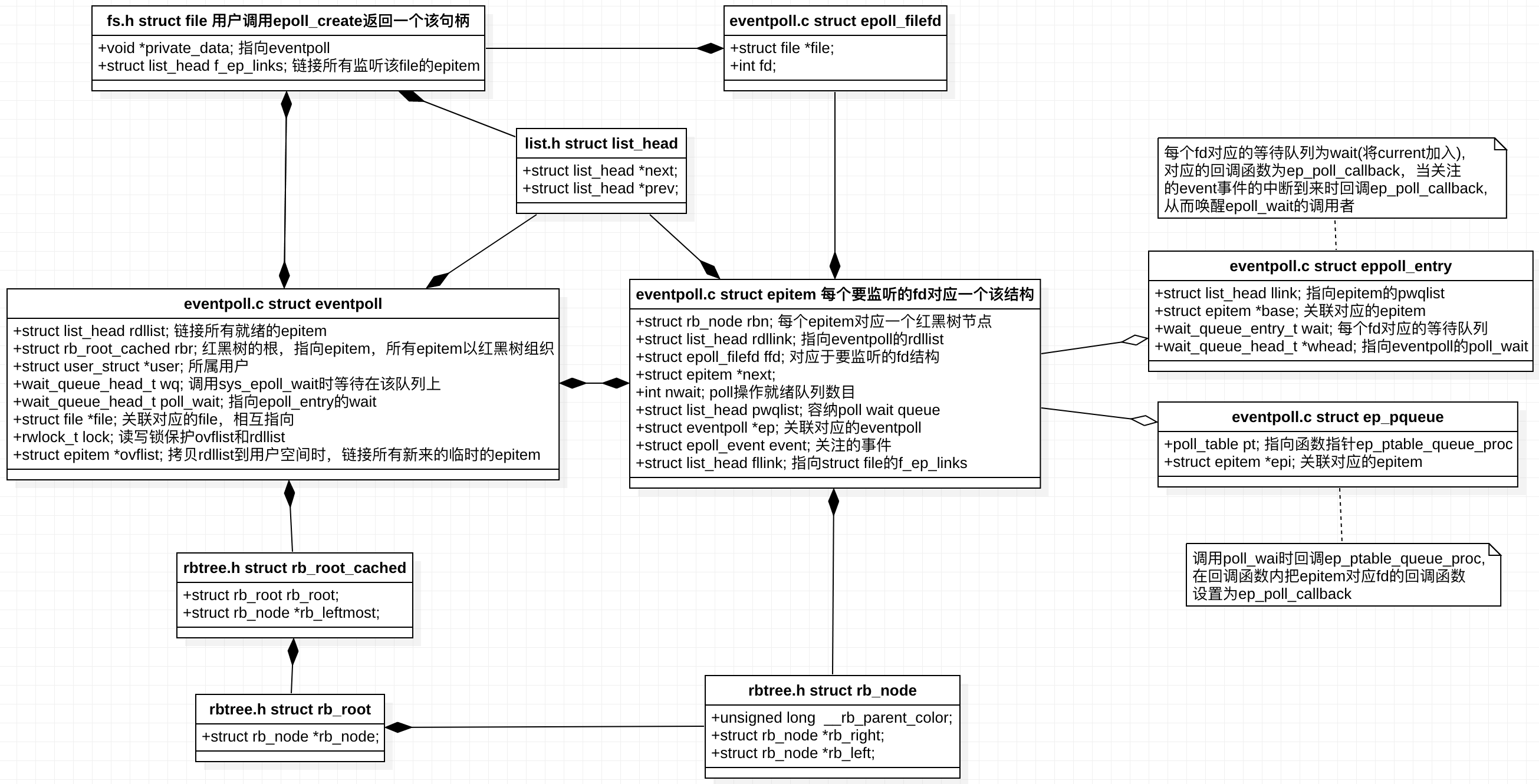
下面贴出各个数据结构代码,切记,实际在过代码的时候,其实我们没有必要对每一个变量和每一行代码咬文嚼字,也不建议这样去做,我们只需要重点关注主要的数据成员和那些关键的代码行,把心思和精力投入到我们最该关注的那部分,从框架层面去把握整体,抓准各个模块的核心,各个模块之间如何耦合,如何同步,如何通信等,这才是能够让你快速进步的最优路线。
1 | /* |
全局调用关系
再贴一张各个API从用户进程陷入到内核态并执行系统调用的详细过程,以及client发数据过来时触发ep_poll_callback回调函数的执行流程。
epoll模块初始化&内存池开辟
epoll是内核的一个module,内核启动时会初始化这个module。
1 | // fs/eventpoll.c |
epoll_create
用户空间调用epoll_create(0)或epoll_create1(int),其实质就是在名为”eventpollfs”的文件系统里创建了一个新文件,同时为该文件申请一个fd,绑定一个inode,最后返回该文件句柄。
epoll_create/epoll_create1陷入内核
1 | // fs/eventpoll.c |
do_epoll_create/ep_alloc
1 | /* |
anon_inode_getfile/alloc_file_pseudo/alloc_file
1 | /** |
epoll_ctl
用户进程调用int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event),op可填EPOLL_CTL_ADD(注册fd到epfd)、EPOLL_CTL_MOD(修改已注册fd监听的事件)和EPOLL_CTL_DEL(从epfd中删除fd)。
epoll_ctl陷入内核
1 | /* |
ep_find
1 | /* |
ep_insert
1 | /* |
kmem_cache_alloc
1 |
|
init_poll_funcptr/ep_ptable_queue_proc/ep_poll_callback/init_waitqueue_func_entry
init_poll_funcptr:设置epq的回调函数为ep_ptable_queue_proc,当调用poll_wait时会调用该回调函数;
ep_ptable_queue_proc:该函数内部所做的主要工作,就是把epitem对应fd的事件到来时的回调函数设置为ep_poll_callback。
ep_poll_callback:主要工作就是把就绪的fd放到就绪链表rdllist上,然后唤醒epoll_wait的调用者,被唤醒的进程再把rdllist上就绪的fd的events拷贝给用户进程,完成一个闭环。
1 | /* |
ep_item_poll/poll_wait/ep_scan_ready_list
1 | /* |
到此,epoll_ctl的分析就已经完了,这里只描述的EPOLL_CTL_ADD调用。EPOLL_CTL_MOD/EPOLL_CTL_DEL相对就简单很多,这三个操作差异主要体现在fs/eventpoll.c文件内接口SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_ctl, int, epfd, int, op, int, fd,struct epoll_event __user*, event)的switch语句部分,EPOLL_CTL_MOD和EPOLL_CTL_DEL分别对应ep_modify和ep_remove,这两个函数就是从红黑树中去找到对应的节点进行修改和删除操作,因此这里没有贴代码。
epoll_wait
epoll_wait陷入内核
1 | // fs/eventpoll.c |
do_epoll_wait/ep_poll/ep_send_events/ep_send_events_proc
1 |
|
参考文献
[1] epoll react
[2] linux epoll源码分析
[3] IO复用select/poll/epoll
[4] IO复用epoll
[5] linux epoll源码
[6] linux poll/epoll实现
[7] linux源码github仓库

